Project Type
Key Points
Background
Greater Western Water (GWW) partnered with Optimatics to optimise solution development during the master planning phase. Their initial proposed plan to increase the compliance of the Youell Street catchment was estimated to cost approximately $9.5 million. However, during the design phase of the works, the cost increased considerably, and a review of the proposed solutions was required. GWW then engaged in a pilot program with Optimizer to analyse the capacity for growth in sub-catchments and refine the initial interventions proposed by the GWW team.
GWW is a water retailer in Melbourne, Australia, providing water, recycled water supply, sewerage, and trade waste services for approximately 630,000 residential and non-residential customers in Melbourne’s west and northwest.
Project Scope
GWW leveraged Optimizer , which utilises genetic algorithms, to analyse and address sewer system performance challenges across various scenarios in the Youell Street catchment.
Prior to partnering with Optimatics, GWW undertook flow monitoring of the Youell Street catchment between 2020 and 2022 because spills were predicted during storm events equivalent to a one-in-five-year average recurrence interval. Based on the data from the 2022 monitoring, GWW updated and recalibrated its hydraulic model, which confirmed deficiencies in the network and enabled solutions to be developed to resolve compliance issues with the Youell Street catchment.
GWW used Optimizer to investigate possible solutions, and the following two analyses were carried out:
- Growth Analysis: Based upon the 2021 population scenario, this analysis considered population growth projects for 2028, 2033, 2043, and 2072. The optimisation aimed to maximise growth while minimising hydraulic penalties. Critical areas where growth could not be accommodated without increasing hydraulic penalties were identified.
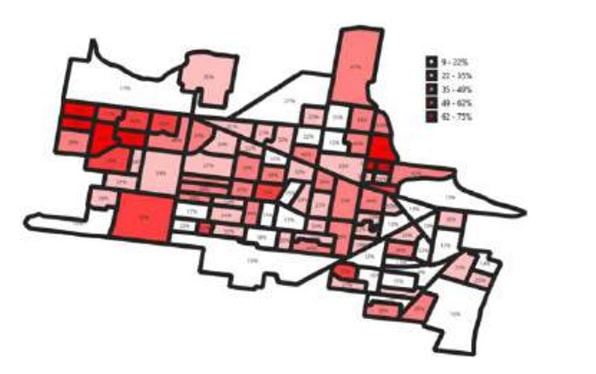
Figure 1 – Percentage of ’Leave as Existing‘ per sub-catchment. Areas in dark red represent areas where optimisation analysis chose more often to ’Leave as Existing’, showing less hydraulic flexibility to accommodate growth.
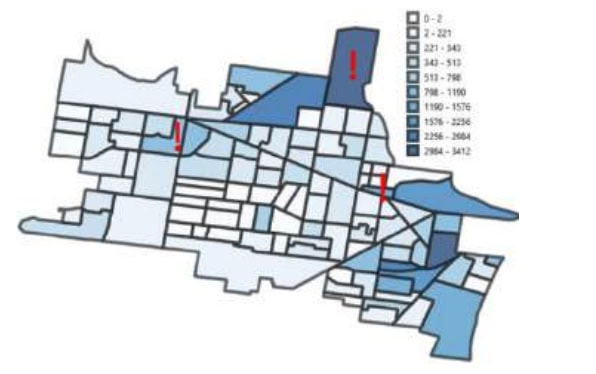
Figure 2 – Growth difference (2023 and 2072) in terms of population added. Highlighted sub-catchments have an increased growth projection based on GWW’s estimates and are within the area with low availability for population growth (based on growth analysis results).
- Master Plan Optimisation Analysis: Using population scenarios for 2023 and 2072, the optimisation process evaluated potential interventions, including integrating new pipelines and upsizing existing ones. The objective was to minimise both total costs and hydraulic penalties.
Outcomes
Optimizer identified areas where additional growth would result in significant hydraulic penalties and discovered alternatives. These new optimal solutions were identified and further adjusted, resulting in lower costs and minimal hydraulic penalties compared to the prior interventions considered. Based on this determination, a stepwise solution was built into three phases. All of the phases reduced the hydraulic challenges in each scenario, while costing GWW significantly less than the initial proposed plan.
An optimised solution was developed and further refined, managing to reduce the overall estimated cost by 21% (from $9.5 million to $7.5 million), while reducing modelled spills to zero in the scenario of year 2072 and staging the delivery of the infrastructure. The introduction of phases to the solutions’ implementation process enabled the deferral of more than half of the capital investment. This produced an outcome that was significantly improved when compared to the original preferred solution in terms of costs reduction and improvement of hydraulic deficiencies.
Following the outcomes of this pilot study, GWW plans to explore the use of similar optimization techniques to support project development in other catchments within their management area.
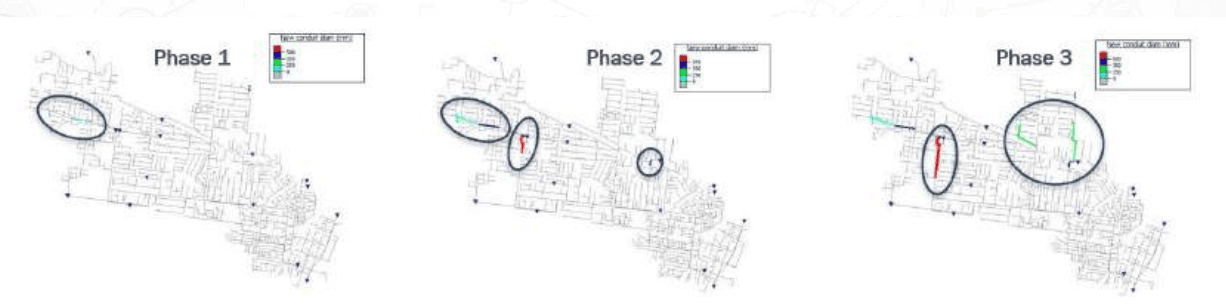
Figure 3 – Phases of works to mitigate non-compliant spills and flooding in the Youell catchment with ongoing growth to 2072.


